.svg?ts=1741967046)
Collecting rainwater - tapping into a valuable resource
Capturing and collecting rainwater is a central component of resource-saving water utilisation. Rainwater is free and available almost everywhere in the world. It is also superior to tap water in terms of quality in certain areas of use. Rainwater harvesting is therefore an independent, decentralised and sustainable addition to the water supply. Rainwater utilisation will become increasingly important in the future due to dwindling groundwater reserves.
Using rainwater is very simple:
Anyone can collect the water from their own roof and use it directly wherever drinking water quality is not required. There are many areas where collected rainwater can be used instead of tap water.
This article deals with the issues surrounding the collection of rainwater, covering the following points:
- Does it actually rain enough in my area to collect rainwater?
- From which surfaces can I collect rainwater?
- Where should I best store the collected rainwater?
- What advantages does rainwater utilisation offer me?
- What legal regulations should I observe?
- Who do I contact to install a rainwater utilisation system?
Wisy recommendations
Our recommendation of low-maintenance products

Is it even raining enough for me to collect rainwater?
Many people grapple with this question before they start collecting rainwater. The fact is, however, that there are no permanently populated areas on earth without rainfall. Accordingly, there is also no place where rainwater cannot be collected.
Much depends on the correct dimensioning of the rainwater collection tank, also known as a cistern, rainwater storage tank or rainwater tank. It is of course necessary to collect and store the rain exactly when it falls from the sky. If you use the right components and install them professionally,
your rainwater can then be stored for many years and can be used as a personal water reservoir in dry periods - e.g. for watering your garden, flushing the toilet and running your washing machine.
With further treatment, rainwater can completely cover all your water needs. Rainwater can therefore make a significant contribution to the water supply anywhere in the world. The local amount and frequency of rainfall, together with the water requirements of the users, determine the size of the cistern required.

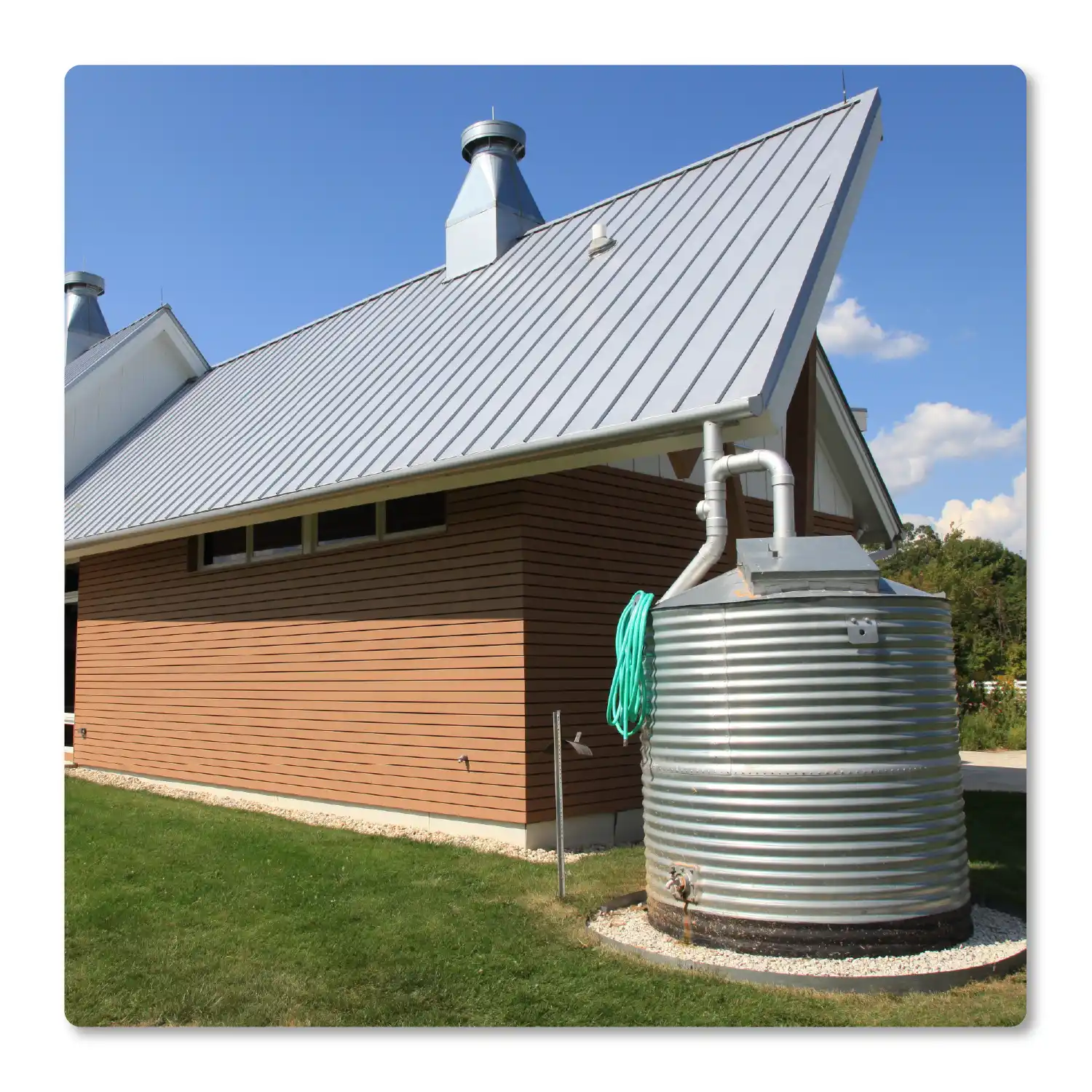
Collect rainwater from the roof
Roofs are the best surfaces for collecting rainwater because they are relatively clean. Rainwater that has just fallen from the sky is not unnecessarily contaminated. In addition, roofs are already equipped with gutters and downpipes, which form part of the rainwater collection system. The gutter directs the collected rainwater via the downpipe to the filter and cistern, where it is first cleaned, collected and stored until it is needed.
The larger a roof is, the more rainwater it can collect. As a rule, it is worth connecting as much of the available roof area as possible to the rainwater storage tank. In addition to the house, all outbuildings, garages, garden sheds, carports, canopies, etc. can also be integrated.
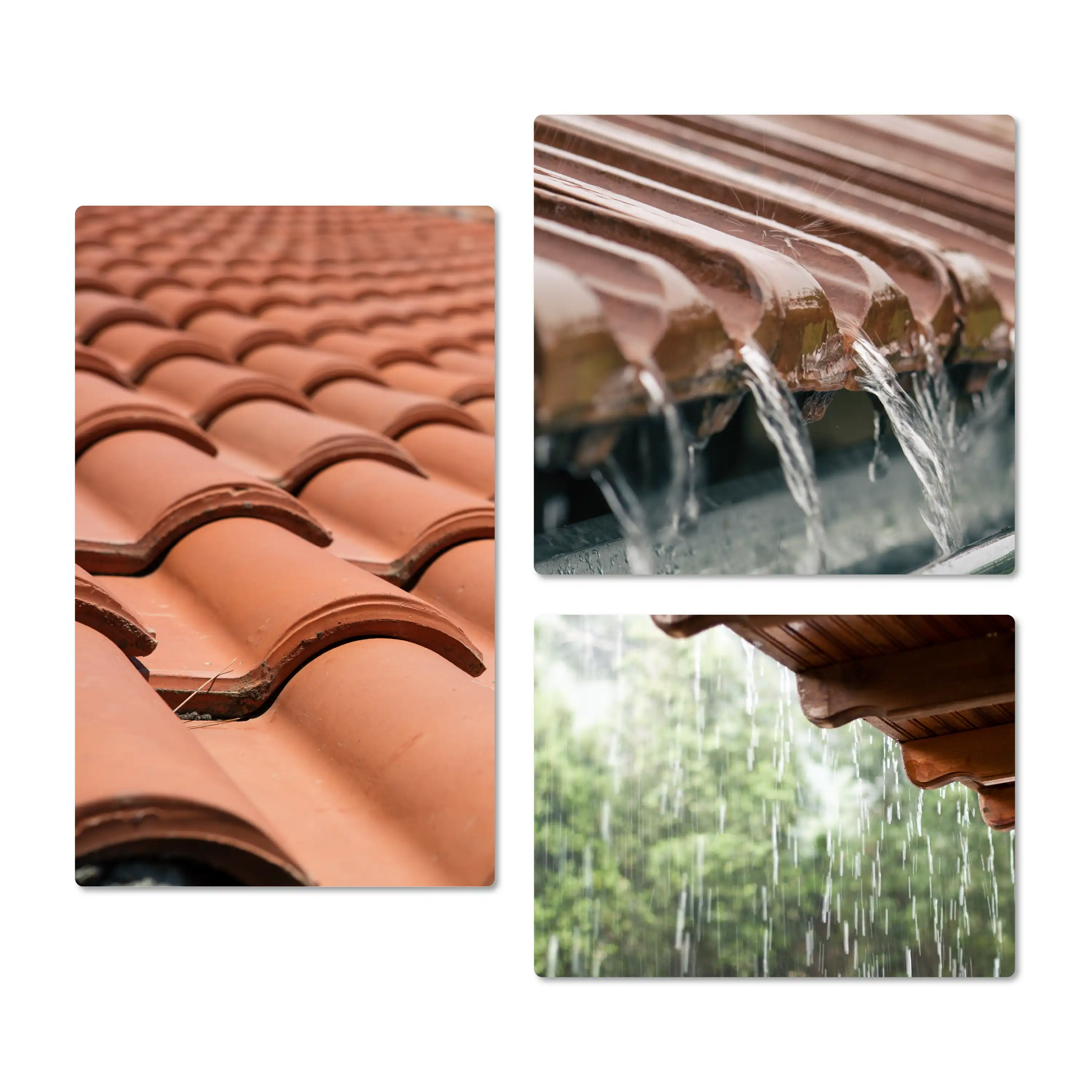

The type of roof covering influences how much rainwater reaches the cistern
Rainwater runs off sloping roof tiles much faster than from a flat roof with gravel or a planted green roof. If the rainwater runs off more slowly, more of it evaporates on its way to the water tank in the garden or underground. In addition, some of the water does not run off the roof at all; the roof is wet after it has rained.
This fact is recorded in a so-called surface yield coefficient. The higher this is for a roof type, the less water evaporates on the way from the roof to the cistern. For example, sloping, smooth surfaces such as conventional tiles have a coefficient of 0.9, which means that 90 % of the precipitation flows towards the cistern, while 10 % evaporates on the way there. A flat roof covered with gravel, on the other hand, has a coefficient of 0.7.
| Collecting surface | Surface value |
|---|---|
| Inclined, smooth roof surface (metal, glass, slate, glazed tiles, solar collectors) | 0,9 |
| Inclined, rough roof surface (concrete roof tiles) | 0,8 |
| Flat roof without gravel | 0,8 |
| Sealed surfaces (asphalt) | 0,8 |
| Flat roof with gravel | 0,7 |
| Green roof, extensive | 0,5 |
| Non-sealed surfaces (paving stone) | 0,5 |
| Green roof, intensive (roof garden) | 0,3 |
The roof material can influence the rainwater quality
The most common roof materials such as roof tiles, glazed tiles, slate, solar panels, glass panes, aluminium or stainless steel profiles are ideal for collecting rainwater. These materials do not release any soluble components and preserve the purity of the water as it falls from the sky.
However, there are also common roof coverings that change the quality of the rainwater.
- With green roofs, it should be noted that the water may become slightly coloured. In this case, the rainwater absorbs colourants from the substrate of the green roof. Rainwater collected from green roofs is not suitable for use in washing machines. When used as toilet flushing water, there may be cosmetic concerns due to the colouring, but it is completely safe to use for garden irrigation.
- The situation is similar with roofs made of bituminous material, whereby "roofing felt" has released all its soluble components after some time and the rainwater can then be used for all areas.
- Metal roofs made of copper, lead or zinc can have increased metal concentrations. There are special ion exchange filters for street run-off water that should be used to treat the water coming from the roof.
- Roofs made of fibre cement (asbestos) must be renovated and are unsuitable for rainwater harvesting due to the washed-out fibres.
Whether the utilisation of rainwater from the special roof surfaces mentioned is possible should be considered on a case-by-case basis. It also depends in particular on the planned use of the rainwater.

Collect rainwater from the balcony
If you have a balcony and would like to collect rainwater from it, you can do this just as easily. Balconies are often already connected directly to existing pipework systems via drains, meaning that rainwater can be collected even without a gutter. There is also no greatly increased pollution compared to roof surfaces, meaning that rainwater from balconies is equally suitable for rainwater utilisation.
Collecting rainwater without a roof
Collecting rainwater without a roof - this is also possible. In principle, however, roofs and comparable collection areas should be the first to be developed for rainwater utilisation, as these have the lowest degree of pollution. However, if the amount of rainwater required exceeds the amount that can be collected by the roof, sealed surfaces such as terraces or footpaths can also be used to collect water. This means you can collect rainwater without a gutter and collect water for the garden without a downpipe.
However, depending on the intended use of the rainwater, existing pollutants from traffic, industry or animals, for example, must be taken into account. Mechanical rainwater filters can reliably remove contaminants above a certain particle size, but contaminants dissolved in the water or containing mineral oil are not so easy to separate.
Rainwater from traffic areas in particular is therefore problematic due to the possible presence of fuel, tyre abrasion or oil. If this water is also to be fed into your rainwater system, additional upstream purification stages must be provided. It must be decided on a case-by-case basis which residues in the collected rainwater are still acceptable and which must be removed by further technical measures.

A tarpaulin to catch the rain?
Another idea would be to collect rainwater without a downpipe using a stretched tarpaulin. This would allow the rain to be channelled directly into a rain barrel without a gutter. Although this is possible, it is more of a temporary or provisional solution. In most cases, the requirements for wind stability are too high for permanent use.
Where should I best store the collected rainwater?
You probably have lots of ideas about what you can use your collected rainwater for. But where is the best place to store the water in your garden? A rainwater barrel above ground or an underground rainwater cistern is a tried and tested way of collecting rainwater.


Collecting rainwater in the rain barrel
The easiest way to collect rainwater in the garden is in a rain barrel. These are available in a wide variety of designs and are ideal for collecting rain directly at the point of use - your garden. On our category page on rain barrels, you can find out what to look out for when buying, where it is best to place the storage tank and how to keep the water in the rain barrel fresh. For example, it is not advisable to simply place a rain barrel without a downpipe under the gutter to let the water simply splash into it, which inevitably leads to regular overflows. In addition, the fresh rainwater could not be cleaned by a downpipe filter.
Collecting rainwater in a cistern
An alternative to the rain barrel is an underground water tank for rainwater - often called a rainwater storage tank or cistern. It is effectively a large underground rain barrel and is an option if you want to store large quantities of rainwater. Cisterns come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes. In our article "Cisterns for rainwater utilisation", we take a closer look at what is important when choosing a cistern, which materials are suitable and how the complete system for collecting rainwater should be designed.

What advantages does rainwater utilisation offer me?

No limescale deposits with rainwater
Anyone who has ever had to deal with encrusted water taps or a calcified garden shower will appreciate the benefits. Not to mention slowly calcifying pipes that become increasingly narrow, which can reduce the flow rate in the domestic pipe network in the long term.
When rainwater is used, there are no limescale deposits because it is soft and lacks the necessary minerals magnesium and calcium. This results in many concrete advantages, all of which speak in favour of collecting rainwater. For example, windows remain completely streak-free after cleaning with rainwater, toilets do not build up limescale and soft rainwater means less washing powder can be used in the washing machine and softeners can be dispensed with completely. Rainwater is also an excellent source of water for watering your plants. Read more about this in our article: Decalcifying and using irrigation water.

Save tap water and protect your wallet
By collecting rainwater for the garden, toilet flushing, washing machine and cleaning, up to 50 % of tap water can be saved in private households. In the public sector, industry and commerce, the potential of a rainwater harvesting system is even higher and can save up to 85% of tap water. This means that you can help to conserve water resources and at the same time significantly minimise your running costs for tap water.
This means that we actually only need 15-50% of the tap water we currently use in drinking water quality. Using rainwater can therefore make a decisive difference here.

Collect rainwater and save on rainwater charges
If rainwater is collected and used on site, property owners can be exempted from the rainwater fee.
The precipitation charge is payable for the disposal of surface water that is collected via gutters and sealed property surfaces and discharged into the public sewerage system. It passes on the costs of the sewage treatment plants to the property owners and is based on the size of the sealed area. Ask your local water supplier about this and find out more in our article on rainwater charges: Costs for rainwater.

More independence in the water supply
Using rainwater not only provides you with a sustainable, but also more independent water supply. As rainwater is purified in four stages to make it suitable for long-term storage over several years, you can simply use the rainwater collected during periods of high rainfall during the dry periods of the year. In this way, you become your own water supplier to some extent and increase your independence.
The special thing about rainwater
Many of the advantages of rainwater can be attributed to one special property: Rainwater is soft!

Toilet flushes remain leak-proof for longer

Pipes last longer

Aerators on fittings + garden showers remain permeable

Toilets without limestone

Save washing powder in the washing machine

Cleaning with less detergent

More good reasons to collect rainwater
- Save tap water: Even in rainy regions, groundwater levels are falling in many places due to overuse
- Save money: Tap water and the disposal of unused rainwater via the sewage system are not cheap
- Save energy: The provision of tap water is very energy-intensive
- Reduce your carbon footprint, read more about this in our article: How to reduce your carbon footprint with rainwater

You should observe these legal regulations
Permits for rainwater utilisation In Germany, you are permitted to collect rainwater without restriction and without a quantity limit. The construction and operation of a rainwater utilisation system does not require a special building permit. However, it is mandatory to notify the local water supplier of the construction of the system in order to comply with any local regulations.
Important standards and technical regulations Compliance with technical and legal standards is crucial. For Europe and Germany, among other things:
- EN 16941 and DIN 1989-100: Regulations for the planning and utilisation of rainwater harvesting systems.
- EN 12056-3 and DIN 1986-100: Rules for roof drainage.
- EN 1717 and DIN 1988-100 as well as the Drinking Water Ordinance: protective measures for the drinking water network.
These standards require a clear separation between rainwater and drinking water. Drinking water may only be fed into the rainwater storage tank in the free outlet above the maximum water level in order to avoid the risk of backwater. In addition, all rainwater pipes and taps must be clearly and permanently labelled to prevent confusion.
Safety measures
- All manhole covers, especially to cisterns, must be closed and open hatches secured.
- Rainwater pipes must be secured against unauthorised use, especially by children (e.g. lockable valves).
- Backwater valves must be installed to prevent backwater from the sewerage system.

Financial support for rainwater utilisation systems
There is no standardised nationwide funding for rainwater harvesting systems in Germany. However, some federal states and numerous local authorities offer financial support for such projects. These subsidies can take the form of grants for the installation of rainwater utilisation systems or concessions on wastewater charges.
Internationally, there are also funding programmes in many countries that aim to separate rainwater from the sewage system and make it usable. These programmes promote measures for sustainable rainwater management and help to conserve freshwater supplies and improve resilience to heavy rainfall events. Such initiatives are widespread in Europe, North America and Australia, for example, and support both private and public projects for near-natural water utilisation.
To find out what funding opportunities are available in your region, it is advisable to enquire directly with the local building, environmental or civil engineering authorities. These offices can provide information on current programmes and the relevant requirements.
Please note that the availability and amount of funding may vary depending on the region. It is therefore advisable to find out about local funding opportunities at an early stage and to submit the relevant applications before starting the measures.
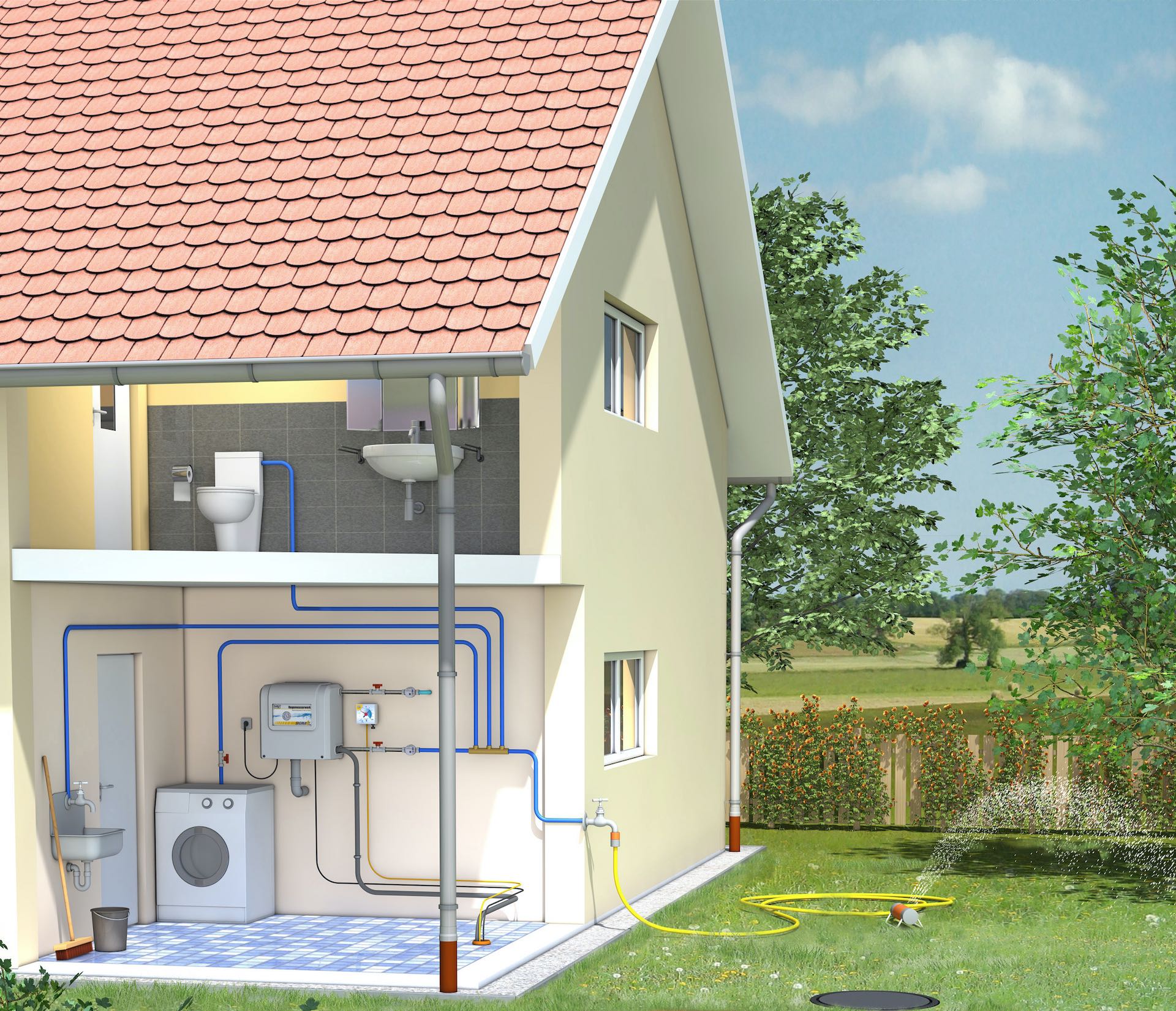
Intelligent use of rainwater
Important components of a rainwater utilisation system
Get advice on rainwater utilisation systems now
WISY AG is your competent partner when it comes to rainwater utilisation. With our many years of experience and personalised advice, we can help you select the right products. Our experts will be happy to advise you by phone and help you find the optimum solution for your requirements.
For detailed planning of your system and professional installation, we recommend contacting local specialists on site. Our comprehensive installation instructions provide all the important technical information that professionals need for a smooth installation.
- Civil engineering company: For the installation of cisterns and underground pipework, you should contact a local civil engineering company.
- Specialist plumbing companies: The installation of water pipes in the house is best carried out by an experienced plumbing company.
With the right local partners and our support in product selection, nothing stands in the way of your successful rainwater utilisation project!